U.S. Faces Era Of Water Scarcity
Profligate use hurts in unexpected places
Quest for new supplies nationwide
UPDATE: Please read our 2009 update on water problems in the US.

Striking symbols of American engineering prowess, Lake Mead and the Hoover Dam stand in testimony to the U.S. spirit of growth and prosperity. But the 28.5 million acre feet Lake Mead is shrinking, as an ever-thirsty nation sprawls across the desert and consumes the waters of the Colorado in an increasingly unsustainable way.
By Keith Schneider
Circle of Blue
Just as diminishing supplies of oil and natural gas are wrenching the economy and producing changes in lifestyles built on the principle of plenty, states and communities across the country are confronting another significant impediment to the American way of life: increased competition for scarce water.
Scientists and resource specialists say freshwater scarcity, even in unexpected places, threatens farm productivity, limits growth, increases business expenses, and drains local treasuries.
In May, for example, Brockton, Massachusetts, inaugurated a brand-new, $60 million reverse osmosis desalinization plant to supply a portion of its drinking water. The Atlantic coast city, which receives four feet of rain annually, was nevertheless so short of freshwater that it was converting brackish water into water people actually could drink.
Builders in the Southeast are confronting limits to planting gardens and lawns for new houses as a result of local water restrictions prompted by a continuing drought. The Ogallala Aquifer, the vast underground reservoir beneath the Great Plains, is steadily being depleted. California experienced the driest spring on record this year.
And scientists at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in San Diego forecast that within 13 years Lake Mead and Lake Powell along the Colorado River, the two largest reservoirs in the southwest United States, could become “dead pool” mud puddles.
“The whole picture is not pretty, and I don’t think that anyone has looked at the subject with the point of view of what’s sustainable,” said Tim Barnett, a research marine geophysicist at Scripps and co-author of the study. “We don’t have anybody thinking long range, at the big picture that would put the clamps on large-scale development.”
Era of Water Scarcity
“I truly believe we’re moving into an era of water scarcity throughout the United States,” said Peter Gleick, science advisor to Circle of Blue and president of the Pacific Institute, a think tank specializing in water issues based in Oakland, California. “That by itself is going to force us to adopt more efficient management techniques.”
The U.S. Drought Monitor, a weekly online report produced by the Department of Agriculture and the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration, shows that severe drought still grips much of the American Southeast, is spreading east from California across the Rocky Mountains, and has also settled in the Texas Panhandle and parts of Oklahoma and Colorado.
While agriculture in the Colorado Basin faces shortages, farmers to the east in the high plains — tapping the Ogallala Aquifer — have progressively seen their wells dry up. The aquifer is the largest in the United States and sees a depletion rate of some 12 billion cubic meters a year, a quantity equivalent to 18 times the annual flow of the Colorado River. Since pumping started in the 1940s, Ogallala water levels have dropped by more than 100 feet (30 meters) in some areas.
In an interview with Circle of Blue, Kevin Dennehy, program coordinator for the Ground-Water Resources Program at the U.S. Geological Survey, said, “The problem with the aquifer is that it’s a limited resource. There is not an unlimited supply, so the recharge is much less than the withdrawals.”
The prognosis for farmers, whose irrigation accounts for 94 percent of the groundwater use on the high plains, does not look optimistic. In the future, irrigation may not be possible at all as the levels continue to drop past the well intakes of farmers. More likely, before the pumping stops, the cost of drilling and maintaining deeper wells may exceed the value of what can be grown, severely limiting the farmland’s value. “There is no other water available,” said Dennehy.
Receding Water in Great Lakes, Other Regions
Declining water levels affect the Great Lakes, too. In a paper published late last year, scientists projected that over the next three decades or so, water levels in Lake Erie, which supplies drinking water to more than 11 million people, could fall three to six feet as a result of climate change.
“We’ll have more wetland and coastal habitat and shallower water,” said John Hartig, manager of the Detroit River International Wildlife Refuge in Michigan. “The falling water levels also have huge implications for power plants. Think of power plants designing their water intakes to draw water from a particular depth, at a particular distance offshore. If you water levels drop 1-2 meters 40 years from now, that’s going to affect all water intakes.”
In an effort to curb draws on the Great Lakes and further protect the basin’s water resources, eight states and two Canadian provinces have passed the Great Lakes compact — an agreement that is intended to prevent the exportation of Great Lakes water to other regions. The compact now needs to be approved by the U.S. Congress before it can become law. (Read an interview about the Compact with James M. Olson, one of America’s preeminent attorneys specializing in water- and land-use law.)
The Southeast has been hard hit as well. Authorities in southern Florida issued water restrictions earlier this year. In August of 2007, city officials in Greensboro, North Carolina fined homeowners associations for watering lawns, washing sidewalks, and other violations of emergency restrictions on water use that were prompted by the region’s severe drought.
In Atlanta, where a severe drought also persists, authorities pressed residents to reduce water use, successfully. Then leaders of the city’s Watershed Management Department, concerned about declining revenue to operate the system, asked permission to raise rates. Officials in Fulton County, where Atlanta is located, did the same thing, praising residents for their efforts at conservation — then increasing their rates by 15 percent. If approved by the city council, the average residential water bill in Atlanta would jump from $84 to $107 next year.
Causes: Climate Change, Population Growth, Profligate Use
Though there is disagreement in the scientific community about when the southeast drought will end, or how low water levels might get in the Great Lakes, most experts say that American water reserves are changing, and in many cases dwindling.
One reason is global warming, which is altering precipitation patterns — producing more droughts in some regions, more flooding in others, and generally making weather patterns unpredictable, thus limiting options for response to extreme conditions. Soil erosion, leaking pipes that are expensive to fix, and an aversion to conservation also are mentioned as causes of scarcity. Another is the country’s growing population, expected to reach 450 million by the middle of the century, or roughly 50 percent more people than now.
The results are unmistakable, especially in California. In June, California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger declared a statewide water emergency, the first since 1991. Though the winter snow pack in the Sierra Nevada, which produces much of the state’s water, was higher than last season, California has had the driest spring on record. Reservoirs are just two-thirds full. Leaders of the state’s fast-growing communities have asked residents to curtail watering lawns and washing cars. In northern California, the air last week was choked by smoke from some 800 forest and grass fires, the highest number on record this early in the fire season.
In 2002, California put into effect a state law that requires developers to prove that new projects have a plan for providing at least 20 years worth of water before local water authorities can approve their projects. For the first time, according to a report in June in the New York Times, several local governments in southern California are actually enforcing the law: They’re requiring developers to prove where new homes will secure their water, and in some cases delaying construction permits.
But even in California, where the state’s 37 million residents live in a real-life theme ride of natural threats – droughts, fires, floods and earthquakes – there is no sense of crisis.
Not Seen as Emergency, Yet
The gravity of the situation hasn’t set in for most Americans. In Atlanta, where drought dramatically lowered Lake Lanier, the region’s primary reservoir, water scarcity is generally seen as temporary, and not related to how the region has grown.
“As an observer of water in the West, as a journalist and a reader of history, I would venture that water scarcity has rarely, if ever, been a long-term limit to growth,” said Jon Christensen, a researcher at the Bill Lane Center for the Study of the North American West at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. “Short-term moratoria on building permits have happened in various places around the West in the past, including Las Vegas. They are usually, in my view, shots across the bows of developers and elected officials that stimulate the search for new deals to bring water from other sources at whatever cost is necessary, so that building can continue.”
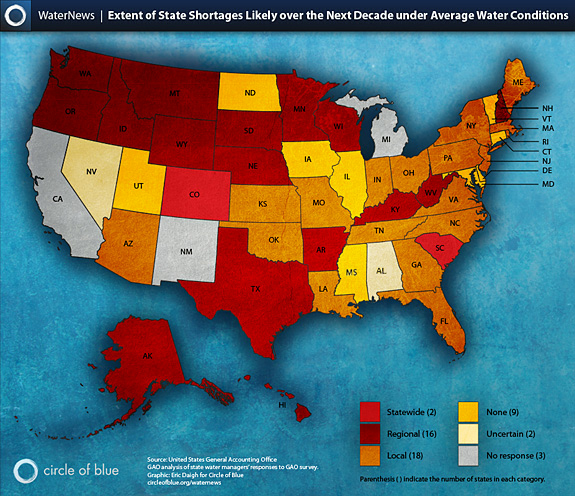
In 2003, the General Accounting Office, an investigative arm of the U.S. Congress, published a survey that found water managers in 36 states “anticipate water shortages locally, regionally or statewide within the next ten years.”
The study has proved disturbingly prophetic, and nowhere more so than on the Colorado Plateau and the rest of the American Southwest. The region is in the ninth year of a persistent drought that continues to leave Las Vegas worried.
On June 6, during a congressional briefing, Gregory J. McCabe, a research scientist with the U.S. Geological Survey, presented a study showing that even a 1.5-degree increase in the overall temperature of the Southwest due to climate change will decrease the Colorado River’s flow. That, he said, increases the likelihood that it will fall short of the amount needed to meet the annual water allocations upon which Nevada, six other states, and 25 million people rely. The Hoover Dam, moreover, will not be able to supply nearly the same level of electric power to Las Vegas as it does today.
“You’ve got a river now that is stretched totally thin, and all the water is being used,” said Barnett, of the Scripps Institution. “There is no excess water. You’re getting less and less water over the decades, so it’s going to be a continuing, festering thing that will get worse,” he added. “That’s desert. It was never meant to have cities. There are millions of people there, and they all have one water supply, only one: the Colorado.”
As Peter Curtiss, an engineer and head of Curtiss Engineering in Boulder, Colorado, noted, “People assume these things are going to be available. We’ve been trained ever since the windmill pumped up water from the farm. Water, electricity and natural gas: When you buy a house, you expect that those services will be there, and the thought of having a house without any one of those seems absurd.”
Managing the Colorado River system and other U.S. water resources in a sustainable way poses great technological, political and social challenges. But, as the Pacific Institute’s Gleick said, “If we continue on our current path, continuing to do things the way we’re doing them, we’re going to be much worse off in five or ten years, or in the coming decades, because the way we manage water now is inappropriate. It’s not sustainable. We over-pump our groundwater. We take water from ecosystems. We don’t think about how we grow and where we grow our population.”
Freshwater scarcity is proving to be the new risk to local economies and regional development plans across the country. Just like the rising price of gasoline, the expanding number of home foreclosures, stagnant incomes, and several other stubborn 21st-century trends, water is imposing limits on how America grows.
“So the business-as-usual future is a bad one,” Gleick continued. “We know that in five years we’ll be in trouble, but it doesn’t have to be that way. If there were more education and awareness about water issues, if we started to really think about the natural limits about where humans and ecosystems have to work together to deal with water, and if we were to start to think about efficient use of water, then we could reduce the severity of the problems enormously. I’m just not sure we’re going to.”
Keith Schneider, a writer in residence at Circle of Blue, and a former national correspondent and regular contributor to the New York Times since 1981, is director of communications at the Apollo Alliance in San Francisco. Additional reporting for this article was provided by C.T. Pope and Aaron Jaffe, researchers in the Circle of Blue office in Traverse City, Michigan. Reach all three at circleofblue.org/contact or contact Keith Schneider directly.
Circle of Blue video interviews about U.S. water issues and the global water crisis:
A conversation with the writer Keith Schneider
A conversation with former NASA astronaut and MIR cosmonaut, Jerry Linenger
Additional Resources:
United States Geological Survey (USGS) Ground-Water Resources Program
Scripps Institution of Oceanography
Bill Lane Center for the Study of the North American West
Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy: The Emerging Water Crisis in the US (PDF)
Circle of Blue’s senior editor and chief correspondent based in Traverse City, Michigan. He has reported on the contest for energy, food, and water in the era of climate change from six continents. Contact
Keith Schneider







Couldn’t states along the coasts build de-salinization plants powered by the sun or wind to be adding to fresh water needs?
I am sure you will see more reverse osmosis desalinization plants in the United States in the coming years. You will also see waste water being turned back into drinking water. The west will have to find new sources of fresh water.
Population is the main issue yet no one ever talks about it–why? We can’t support more people with food, water, jobs, etc. We have tv shows that celebrate families with 17 children instead of telling people to only have one or two.
We need to start recycling our dirty water and reusing it.
Great post. I’m going to link to this article, as well as the maps and mapping tools.
More freshwater awareness stuff like a water use calculator, kids games, and a review of a cool new Imax about the Colorado River.
http://blog.mywonderfulworld.org/2011/06/colorado-river-adventure-learning-and-advocacy.html